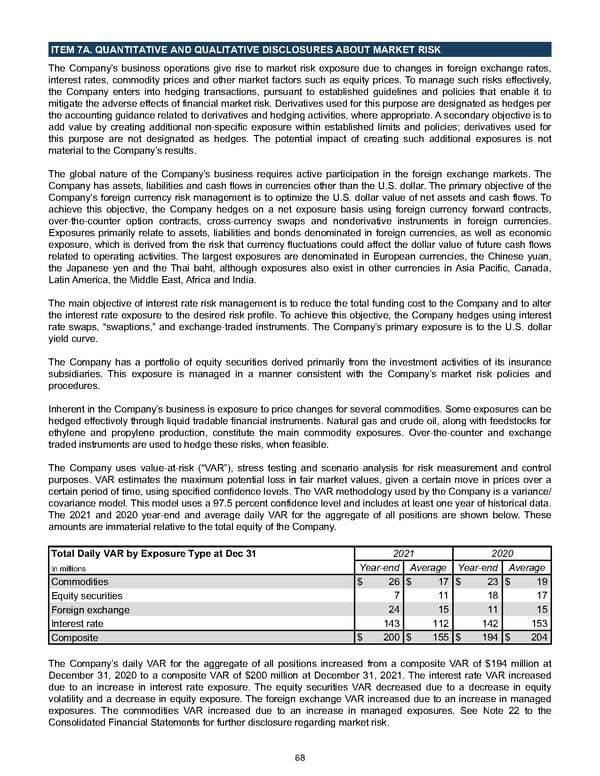
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK The Company’s business operations give rise to market risk exposure due to changes in foreign exchange rates, interest rates, commodity prices and other market factors such as equity prices. To manage such risks effectively, the Company enters into hedging transactions, pursuant to established guidelines and policies that enable it to mitigate the adverse effects of financial market risk. Derivatives used for this purpose are designated as hedges per the accounting guidance related to derivatives and hedging activities, where appropriate. A secondary objective is to add value by creating additional non-specific exposure within established limits and policies; derivatives used for this purpose are not designated as hedges. The potential impact of creating such additional exposures is not material to the Company’s results. The global nature of the Company’s business requires active participation in the foreign exchange markets. The Company has assets, liabilities and cash flows in currencies other than the U.S. dollar. The primary objective of the Company’s foreign currency risk management is to optimize the U.S. dollar value of net assets and cash flows. To achieve this objective, the Company hedges on a net exposure basis using foreign currency forward contracts, over-the-counter option contracts, cross-currency swaps and nonderivative instruments in foreign currencies. Exposures primarily relate to assets, liabilities and bonds denominated in foreign currencies, as well as economic exposure, which is derived from the risk that currency fluctuations could affect the dollar value of future cash flows related to operating activities. The largest exposures are denominated in European currencies, the Chinese yuan, the Japanese yen and the Thai baht, although exposures also exist in other currencies in Asia Pacific, Canada, Latin America, the Middle East, Africa and India. The main objective of interest rate risk management is to reduce the total funding cost to the Company and to alter the interest rate exposure to the desired risk profile. To achieve this objective, the Company hedges using interest rate swaps, “swaptions,” and exchange-traded instruments. The Company’s primary exposure is to the U.S. dollar yield curve. The Company has a portfolio of equity securities derived primarily from the investment activities of its insurance subsidiaries. This exposure is managed in a manner consistent with the Company’s market risk policies and procedures. Inherent in the Company’s business is exposure to price changes for several commodities. Some exposures can be hedged effectively through liquid tradable financial instruments. Natural gas and crude oil, along with feedstocks for ethylene and propylene production, constitute the main commodity exposures. Over-the-counter and exchange traded instruments are used to hedge these risks, when feasible. The Company uses value-at-risk (“VAR”), stress testing and scenario analysis for risk measurement and control purposes. VAR estimates the maximum potential loss in fair market values, given a certain move in prices over a certain period of time, using specified confidence levels. The VAR methodology used by the Company is a variance/ covariance model. This model uses a 97.5 percent confidence level and includes at least one year of historical data. The 2021 and 2020 year-end and average daily VAR for the aggregate of all positions are shown below. These amounts are immaterial relative to the total equity of the Company. Total Daily VAR by Exposure Type at Dec 31 2021 2020 In millions Year-end Average Year-end Average Commodities $ 26 $ 17 $ 23 $ 19 Equity securities 7 11 18 17 Foreign exchange 24 15 11 15 Interest rate 143 112 142 153 Composite $ 200 $ 155 $ 194 $ 204 The Company’s daily VAR for the aggregate of all positions increased from a composite VAR of $194 million at December 31, 2020 to a composite VAR of $200 million at December 31, 2021 . The interest rate VAR increased due to an increase in interest rate exposure. The equity securities VAR decreased due to a decrease in equity volatility and a decrease in equity exposure. The foreign exchange VAR increased due to an increase in managed exposures. The commodities VAR increased due to an increase in managed exposures. See Note 22 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further disclosure regarding market risk. 68
 Annual Report Page 77 Page 79
Annual Report Page 77 Page 79